What is a Motor Pump and How Does it Work?
Motor pumps are vital to various industries, providing efficient fluid movement. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global motor pump market is projected to reach $55 billion by 2027. This growth highlights the increasing demand for reliable pumping solutions in sectors like agriculture, manufacturing, and energy.
Dr. Jane Smith, a leading expert in fluid dynamics, remarks, “Motor pumps are crucial for optimizing operational efficiency.” The role of motor pumps extends beyond simple fluid transfer; they ensure safety and enhance productivity in numerous applications. In construction, for instance, reliable motor pumps prevent project delays due to water accumulation. However, not all motor pumps operate at peak efficiency. Maintenance issues can lead to increased energy consumption and performance loss.
Understanding how motor pumps work is essential. They convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, moving liquids effectively. Despite advancements, challenges remain in sustainability and energy efficiency. Investing in high-efficiency models can mitigate some issues. Hence, knowledge of motor pump operation and selection is indispensable for maximizing their benefits in any application.
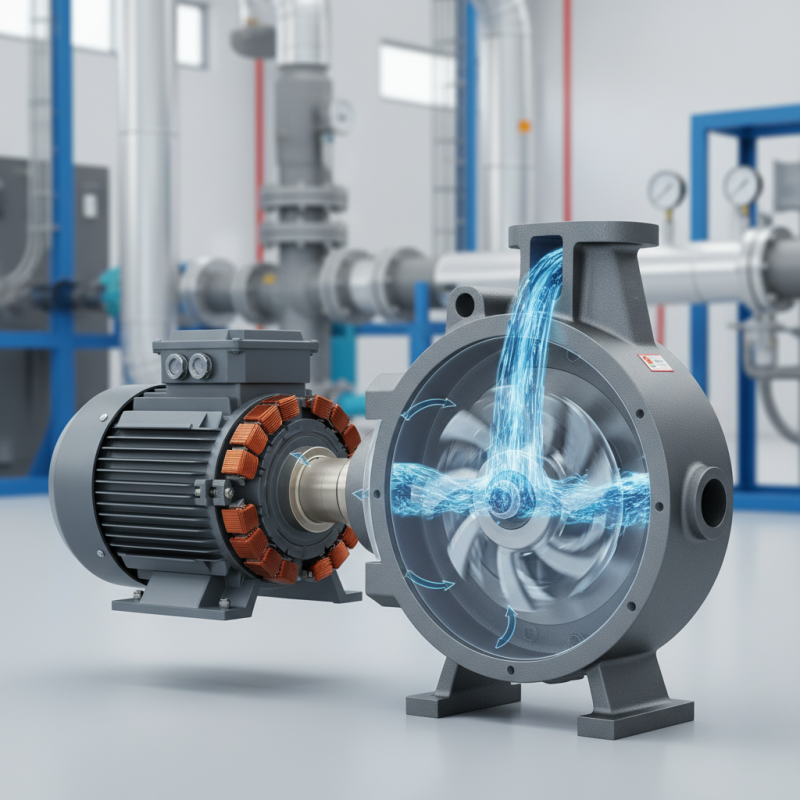

What is a Motor Pump?
A motor pump is a device that moves fluids using mechanical energy. It consists of a motor and a pump, working together. The motor powers the pump, creating suction and pressure to move liquids. This process can be seen in various applications, such as irrigation systems and water supply.
The design of a motor pump is relatively straightforward. The motor usually converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. This energy causes the pump to draw fluid from a source. The mechanism can be simple, but choosing the right motor pump is crucial. Many factors, like power requirements and fluid types, need consideration.
Not everyone understands the importance of maintenance. Neglecting regular checks can lead to inefficiency. Performance may decline over time due to wear and tear. It's important to regularly inspect motors and pumps. Small issues can escalate, causing larger problems later on. Understanding this relationship is vital for effective operation.
Motor Pump Efficiency Comparison
Components of a Motor Pump
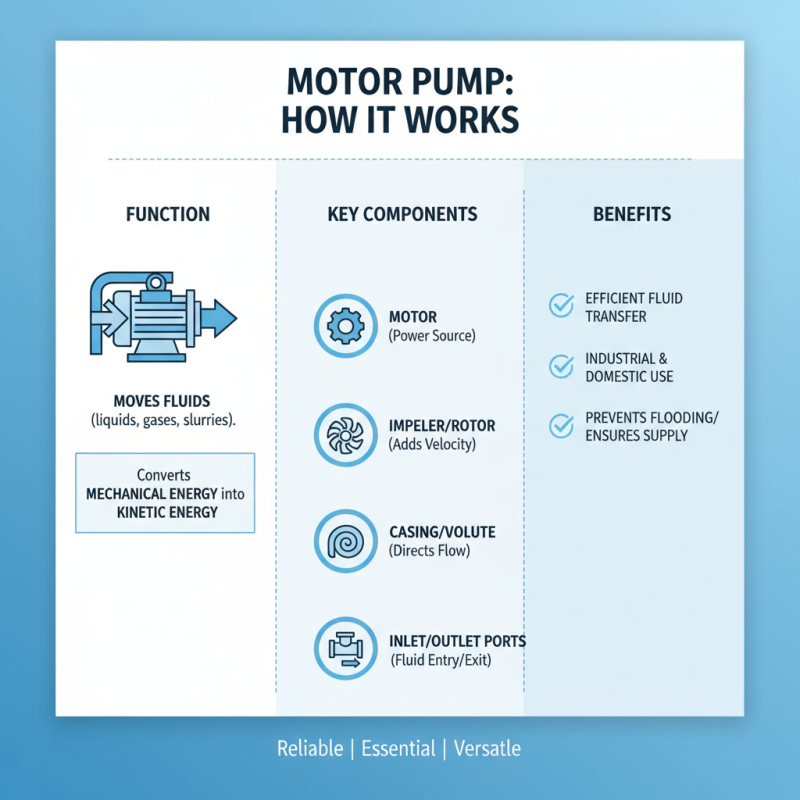
A motor pump is a vital device used to move fluids. It operates using mechanical energy converted into kinetic energy. Understanding its components can help ensure effective operation.
The core of a motor pump is the motor, which drives the pump mechanism. Usually electric, the motor powers a shaft connected to a pump impeller. This impeller is crucial; it creates a centrifugal force that moves the fluid. Next, we have the casing, which holds everything together. It prevents leaks and houses the impeller.
Tips: Regular maintenance is essential. Clean the impeller and check for wear. Also, ensure the motor is properly lubricated. Overworking can lead to breakdowns. Don’t ignore unusual noises; they can signal problems.
Another vital component is the inlet and outlet ports. They control fluid entry and exit. Proper sizing is critical; too small can restrict flow. Additionally, various seals and gaskets prevent leaks. If damaged, they can cause significant issues.
Consider the environment when choosing a motor pump. Temperature and fluid type matter. These factors can impact durability and efficiency. Always assess the pump’s suitability for your specific needs.
How Motor Pumps Operate: The Mechanism Explained
Motor pumps are essential devices used to move fluids from one place to another. Understanding how they operate can enhance their efficiency and help us utilize them effectively. Engineered primarily with an electric motor, these pumps transform electrical energy into mechanical energy. This transformation initiates the movement of a rotor, which is crucial in propelling the fluid through the pump.
The mechanism consists of several key components. The motor spins the rotor, creating a difference in pressure. This pressure difference draws fluid into the pump's casing. As the rotor continues to spin, it forces the fluid out of the discharge port. Observing this process can reveal inefficiencies. Occasionally, air may enter the system, leading to cavitation and reduced performance. Regular maintenance is vital in avoiding such issues and ensuring the fluid moves seamlessly.
However, motor pumps can present challenges. They require consistent monitoring to ensure they operate within specified limits. Over time, wear and tear on parts can impact performance. It is a reminder that even robust machinery needs attention. By identifying and addressing these problems, users can enhance reliability and efficiency. In a world that relies heavily on these devices, understanding their mechanism is key to successful operation.
Different Types of Motor Pumps and Their Uses
Motor pumps come in various types, each designed for specific tasks. Centrifugal pumps are popular for transferring liquids at high rates. They use a rotating impeller to create flow. These pumps are efficient and widely used in agriculture and industrial applications.
Positive displacement pumps are another category. They move fluids by trapping a fixed amount and forcing it through the outlet. These pumps are effective for viscous liquids. They find uses in food processing and chemical industries. Choosing the right type depends on the fluid's properties and application needs.
Submersible pumps operate underwater. They're ideal for dewatering applications and groundwater extraction. However, maintenance can be challenging, as they require regular checks. Each type of motor pump has its strengths but may also present limitations. Understanding these can help in making better choices for specific needs.
Applications of Motor Pumps in Various Industries
Motor pumps are essential in many industries. They help move liquids from one place to another. These devices use an electric motor to drive the pump mechanism. Motor pumps are commonly found in agriculture, construction, and manufacturing. They offer efficiency and convenience.
In agriculture, motor pumps supply water for irrigation. Farmers can manage water usage better. This approach boosts crop yields. In the construction sector, they help in dewatering worksites. A reliable motor pump can prevent flooding in trenches. However, maintenance is vital. Neglecting it can lead to breakdowns.
Tips: Regular checks on seals and bearings extend pump life. Monitor for unusual noises. This helps catch problems early. In manufacturing, these pumps transfer chemicals. Proper training for operators is essential. Basic knowledge of hazards is critical. Overlooking safety might lead to accidents. Exploring these aspects can enhance operational efficiency.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Motor Pump Brands You Should Consider for Efficiency and Reliability
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Goulds Water Pump for Your Needs
-

Top 10 Trash Pumps for Efficient Wastewater Management Solutions?
-

Understanding Goulds Water Pumps Efficiency and Longevity in Modern Applications
-

Best Electric Water Pumps for Home Use in 2023 Reviews and Buying Guide
-

Ultimate Guide to Using a Pump Catalog with Actionable Tips for Success
COMPANY INFO
Copyright © 2025. Rotech Pumps & Systems Inc. All rights reserved.

